Getting your website into the Google Knowledge Graph is not a wishful thinking anymore. It’s a necessity.
As we move away from the keyword-based search and enter the realm of semantic entity search, the game of SEO is transforming. Simply having good content on your website is no longer enough. The key to dominating the search results is to communicate with search engines using entities, which is like ‘SEO on steroids’.
If you want to be a cut above the rest and secure your position in the Google Knowledge Graph, showcasing rich snippets for your search results is the quickest and most reliable method. This isn’t just our opinion, but it’s also what Google recommends, as evident from this inspiring video here: http://goo.gl/loE0ME. So, embrace the power of entities and enrich your search results with structured data to take your SEO game to the next level!
What are rich snippets?
Rich snippets (also called rich results) are any type of search listing in the Google SERPs that displays visual or interactive data. Unlike regular search results, rich snippets display more detailed and visual information, such as images, star ratings, reviews, product information, and more.
Rich snippets are designed to make search results more informative and engaging for users (resulting in more ‘relevant’ visits to our websites), helping them to quickly and easily find the information they are looking for. Rich snippets are generated by search engines using structured data markup on a website, which tells search engines what type of content is on the page and how it should be displayed in the SERPs.
The Google’s Definition of Rich snippets:
Snippets – the few lines of text that appear under every search result – are designed to give users a sense for what’s on the page and why it’s relevant to their query.
Notice the word “relevant.” Relevant is the foundation on which Google’s semantic search engine is built. Traditional search algorithms match your search query with ‘keywords’ extracted from web pages and organize those results in order of relevance. On the other hand, semantic search tries to understand your query in more depth, showing you more meaningful and relevant results.
Looking at it from a different point of view, it is a way for webmasters to ‘advertise’ their pages and products better, giving us more information before we decide to click through to a website.
Can we see these results in the SERPs? Hell yeah. Just go to Google and search for ‘music festivals in London’.
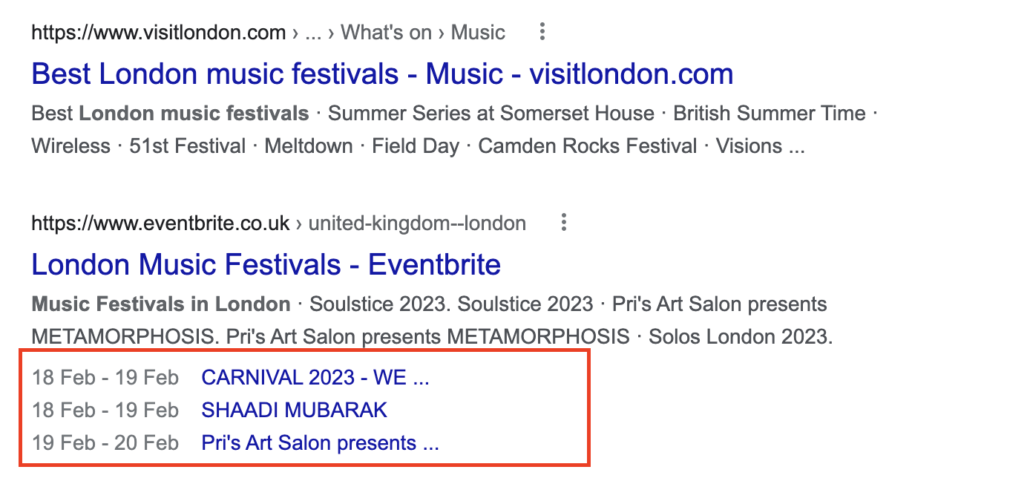
Now, take a look at the second result. See, even if I hadn’t told you, you would have looked at the fourth result anyway. Although the first result is more relevant to your query (hence the first position in Google), your eyes are automatically drawn to the more organised and, in a way, more attractive second position.
Another example is searching for tomato soup: your eyes are automatically drawn to the picture, especially if you are hungry.
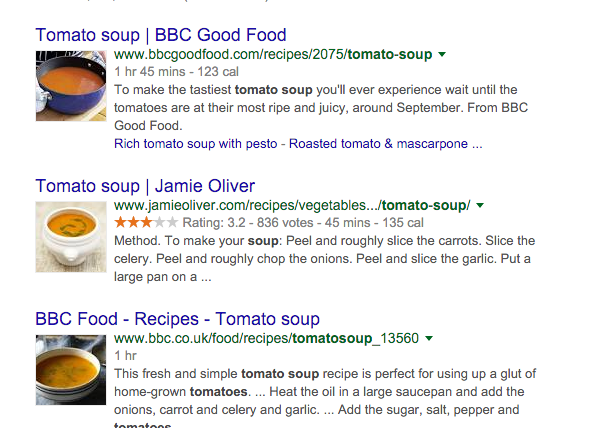
3 key benefits of Rich snippets
Not even intentionally we’ve already tapped in the main benefits of the rich snippets.
- Make your content advertise itself. More visual, eye-catching results in the SERPs.
- Increased Organic CTR. More visual and more relevant information will probably increase the CTR (Click Through Rate). Having a peek before visiting a page will definitely decrease the bounce rate of a particular page. Google says bounce rate is not considered when ranking a page, but I am not so sure. Since introducing Panda 4.0. we see increased organic visibility for pages based on the so-called ‘user signals’. One of those signals is the so-called ‘Return-to-SERP rate‘ – the proportion of searchers going back to the search engine results page after having clicked on a link – which suggests they did not find what they were searching for. Or in other words, less relevance means a higher bounce rate and potentially lower rankings. Do you see the benefit of allowing the searcher to know what to expect on your page?
- Bring ‘qualified traffic’. Rich snippets will not only increase your CTR, but they will also bring more ‘qualified’ traffic too. The people visiting your pages (especially e-commerce) are making an educated decision to click through to your website knowing your product, pricing and availability in advance. They wouldn’t have clicked on your link if they didn’t want to make a purchase. Going even more backward they wouldn’t have been even online looking for your product-specific term.
Tip: Feels like I have to give you an advice here: know your customers.
Rich Snippets: How to Implement?
I will try to be as less geeky as possible and I also promise to show you the easiest method.
First let’s clear up some terms/definitions before we go to the really technical part.
Rich snippets as we know them were introduced by Google in 2009. In a surprising move in year 2012 all major search engines came together (for a richer web: http://goo.gl/JevRHR) and announced a new initiative called schema.org. Schema.org main purpose is “to create and support a common vocabulary for structured data markup on web pages”. This initiative started with a small number of formats, but the idea to support a wider range of schemas over time.
Fast forward to 2014 and the official schema supported by Google is JSON-LD.
You have to understand that using JSON-LD, Microdata or RDFa produces exactly the same result. It’s just that JSON-LD is the preferred language by Google and although I never worked with Microdata and RDFa I believe I it is absolutely the easiest markup to implement in your applications.
To enable Rich Snippets for your content in search results, you need to add the appropriate markup to your pages. Currently, there are around 29 main categories and two additional markups for COVID-19 announcements and Speakable structured data. Below is a list of some of the most popular strucured data.
- Course Info structured data – structured data markup that is used to describe educational courses in a way that is easily understandable for search engines.
- Vehicle listing structured data – structured data markup that is used to give Google information about new car listings for improved visibility within the Google Search results.
- Product structured data – Information about a product, including price, availability, and review ratings.
- Recipe structured data – Recipes that can be displayed in web searches and Recipe View.
- Review snippets – A review of an item such as a restaurant, movie, or store.
- Event structured data – An organized event, such as musical concerts or art festivals, that people may attend at a particular time and place.
- Software App structured data – Information about a software app, including its URL, review ratings, and price.
- Video structured data – Information about description, thumbnail URL, upload date and duration. Google may decide to use your rich snippet markup to power ‘content carousel’.
- Article structured data – You can provide details like a headline, images, publish date and description. If you are lucky enough “Google may use your rich snippet markup to power features like “In the news” and content carousels”.
After deciding which type is most appropriate to your content your very first stop should be The Google Structured Data Markup Helper. As JSON-LD is a new language to almost everybody (including many webmasters), not many people know and understand how to markup their webpages content correctly. Don’t be inventive.
The Structured Data Markup Helper is there to help you make the markup process easier so the search engines can read it correctly.
Structured Data Markup Helper
Start by selecting the data you are working with, then paste the URL (or the HTML) of the page you want to mark up. Click on the button “Start Tagging” and you are presented with a page like that:
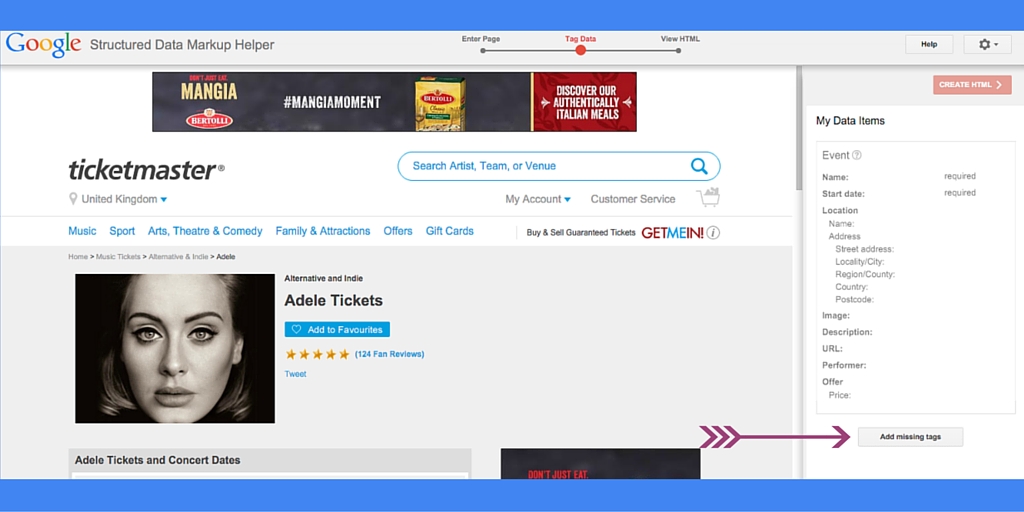
Here you have got two options. One is to highlight the text that you want to mark and the other one (the less intuitive one) is to click on the Button “Add missing tags” and add all the tags piece by piece.
To make the first method a bit more clear have a look at the image below. I have highlighted the text that I’d like to have as a “Name” the article. Straight away I am given a drop down menu with options for tagging the selected text. All I have to do now is select the “Name” tag and you gonna see it displayed as “Name” in the right-hand side corner of the page.
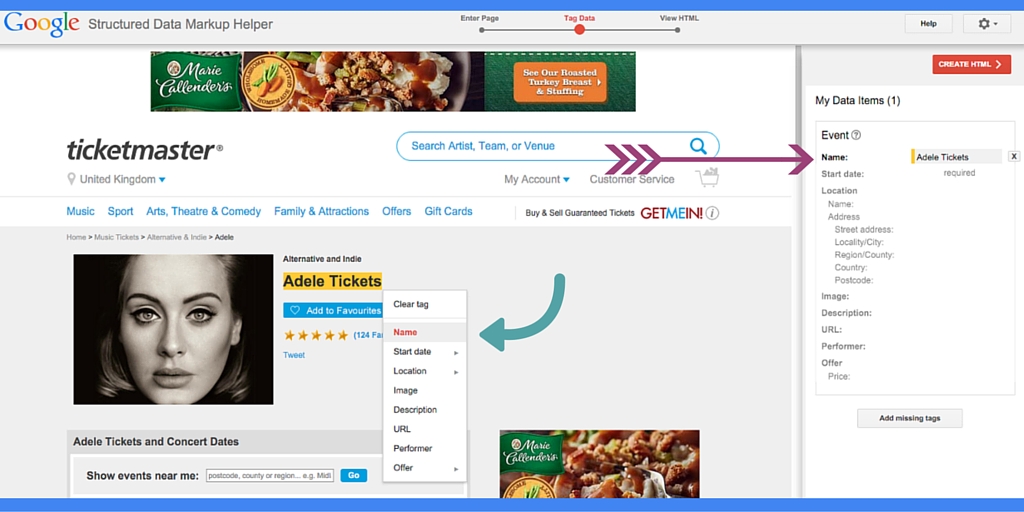
Note: You don’t have to assign some value to every single tag if this tag doesn’t apply to your content. For example, you may not have a picture in your article or you may not need/use “Aggregate Rating” in your blog.
When you finish tagging all your content (if anything is missing just use the “Add missing tags” option) click on “Create HTML”. Now we are provided with the HTML source code with the markup of our choice- either Microdata or JSON-LD.
Have a look at both ways of marking up your pages. Don’t you find Microdata a bit confusing?
Click on JSON-LD and you are presented with “Structured data as JSON-LD Markup”.
Markup example: Event
<script type="application/ld+json">
[{
"@context" : "http://schema.org",
"@type" : "MusicEvent",
"name" : "Adele Tickets",
"startDate" : "2016-04-12T19:30",
"location" : {
"@type" : "Place",
"name" : "The SSE Arena",
"address" : "79 Liverpool St., London"
},
"offers" : {
"@type" : "Offer",
"url" : "http://www.ticketmaster.co.uk/Adele-tickets/artist/1159272"
}
}]</script>
As Google is suggesting “Add the script block below to the head section of your html”.
I have highlighted the elements that can be created dynamically by your back-end system but of course, you can tag all your web pages manually (not recommended – prone to mistakes).
Use the Rich Results Test to test and validate your structured data
Your next step should be going to the Rich Results Test Tool in order to validate the structured data markup code of your pages. According the Google the main features of this tool are:
- Validation for all Google features powered by structured data
- Support for markup in the JSON-LD syntax, including in dynamic HTML pages
- Clean display of the structured data items on your page
- Syntax highlighting of markup problems right in your HTML source code
In practise, all you have to do is paste a link or HTML code in order to validate your markup code.
Go and validate the code I have given you above. Did you notice the ‘Missing field ‘priceCurrency’ (optional)‘ warning?
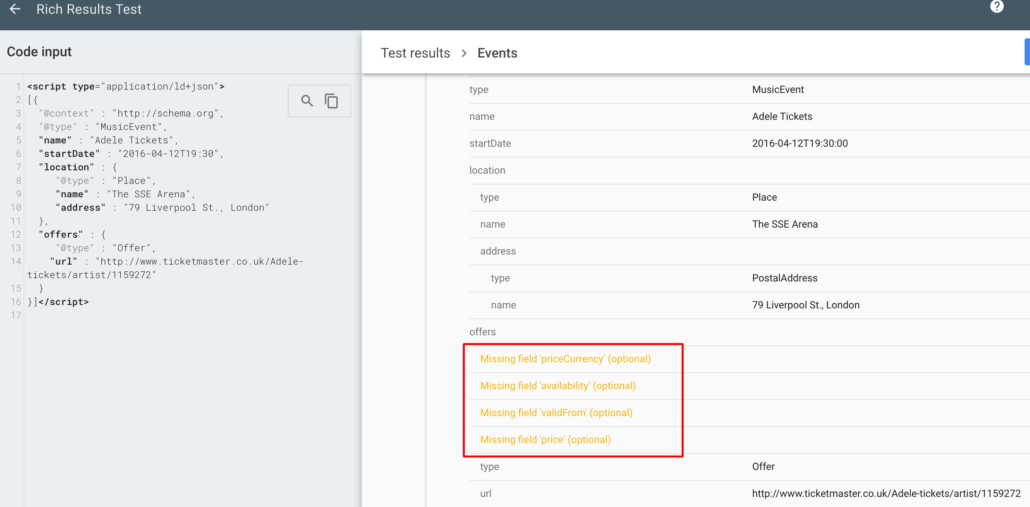
You have to agree with me that this is one very intuitive and easy to use tool from Google.
Tip: Come on, don’t be shy. Go and check out your competitor’s’ pages as well.
This article wouldn’t be complete without one of my favourite developments by Google.
Specify your social profiles to Google to display in Google Knowledge Graph
You can add your company’s (or personal) social profile information to your Google Knowledge Graph by using structured data markup on your official website. Make sure you fulfill these requirements:
- Publish markup on a page on your official website
- Pages with markup must not be blocked to the Googlebot by robots.txt
- Include a Person or Organization record in your markup with:
- “url” = the url of your official website
- “sameAs” = the urls of your official social media profile pages
Note: “The SCRIPT block can be inserted anywhere on the page — either the head or body of the page”.
Markup example: Person
<script type="application/ld+json">
{ "@context" : "http://schema.org",
"@type" : "Person",
"name" : "Omi Sido",
"url" : "https://omisido.com/",
"sameAs" : [ "http://uk.linkedin.com/in/omisido",
"https://www.linkedin.com/in/aaranged",
"https://twitter.com/OmiSido",
"https://plus.google.com/+OmiSido"]
}</scrip>Conclusion:
The benefits coming from implementing rich snippets make them incredibly useful for SEO.
Rich snippets assist the web crawlers to easily understand and index the content on our web pages thus presenting more ‘clickable’ and attractive results in the SERPs.
Rich snippets ensure the visitor has a prior knowledge of what to expect on a page and a direct effect on our CTR. What SEO does not want that? However, bare in mind that just adding structured data alone won’t directly influence your organic rankings, but the indirect effect of higher CTRs and less pogo sticking will help you rank better.


Leave a Reply