Understanding where your website traffic originates from in today’s data-driven marketing world is crucial for optimising your digital marketing campaigns and enhancing the user experiences of your visitors. While traditional analytics focus mostly on organic search and PPC advertising, there is a new kid on the block called ‘AI-driven traffic’.
Probably there is no need to tell you that AI traffic originates from interactions with so-called artificial intelligence platforms like chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated programs. As more and more people use AI chatbots to find answers that are difficult to find in search engines, accurately tracking AI traffic and its impact on your website becomes without a doubt essential.
But how do you identify referral traffic specifically from AI sources in Google Analytics 4 (GA4)?
Why Track AI Referral Traffic?
AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini and Perplexity are rapidly transforming how users interact with websites. Chatbots handle customer inquiries, virtual assistants recommend products and automated programs curate personalised experiences. Traffic generated by these AI interactions falls under the umbrella of referral traffic in Google Analytics 4. However, isolating and analysing it presents unique challenges.
I will show you how to track AI referrals in GA4 but first here’s why, in my opinion, tracking AI referrals in GA4 is crucial:
- Measuring AI’s traffic effectiveness helps you to evaluate how AI interactions influence user engagement, conversion rates, and overall website performance.
- Gaining insights into which AI interactions drive the most valuable traffic will allow you to make targeted improvements to your website.
- By tracking AI referral traffic over time you can understand its evolving role in your website’s traffic mix. I expect AI traffic to rise significantly over time. Pay attention!
- By comparing AI referral traffic to organic search, paid advertising (PPC), and other channels you can assess its relative contribution.
- To stay ahead of your competitors you should be monitoring industry trends in AI referral traffic. Measure your performance against them so you can understand how AI traffic influences user journeys, so you can employ data-driven strategies that enhance your website for both AI-driven and human interactions.
How to track AI traffic in GA4
Create an exploration report and use a regex formula to filter traffic
Currently, the easiest way to track traffic coming from AI tools, as far as I know, is to create an exploration report in GA4 with a regex formula to work with traffic source data, as shown in the screenshot.
- Start by creating a new Exploration report (I will call it AI Traffic).
- Set your ‘Dimensions’ to ‘Session source / medium’ and use ‘Views’ as a metric.
- In ‘Filters’, choose ‘Matches Regex’, and in the ‘Enter Expression’ box, copy and paste the following regex:
.*gpt.*|.*chatgpt.*|.*openai.*|.*neeva.*|.*writesonic.*|.*nimble.*|.*outrider.*|.*perplexity.*|.*google.*bard.*|.*bard.*google.*|.*bard.*|.*edgeservices.*|.*gemini.*google.*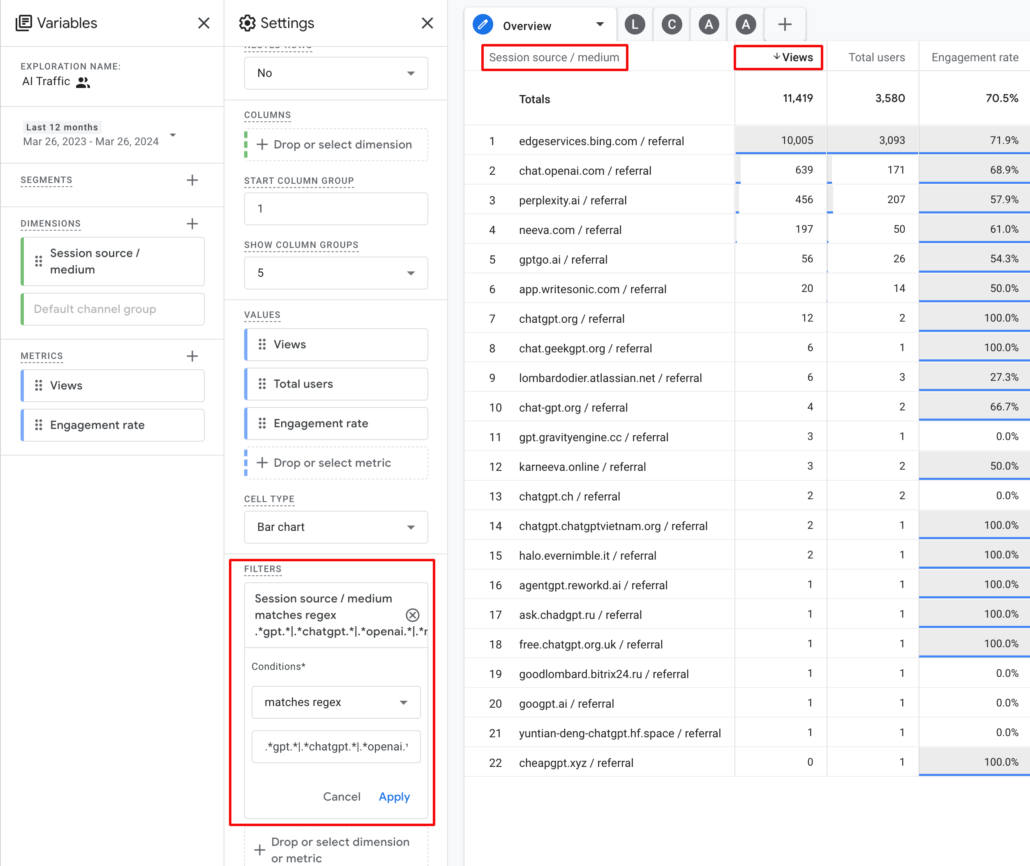
Pro Tip: Remember that AI traffic identification is still evolving. This Regex pattern searches for keywords commonly associated with popular AI platforms like GPT, ChatGPT, OpenAI, and Gemini Gemini (Formerly Bard). Don’t hesitate to update this list as new AI players emerge.
Create an AI traffic segment
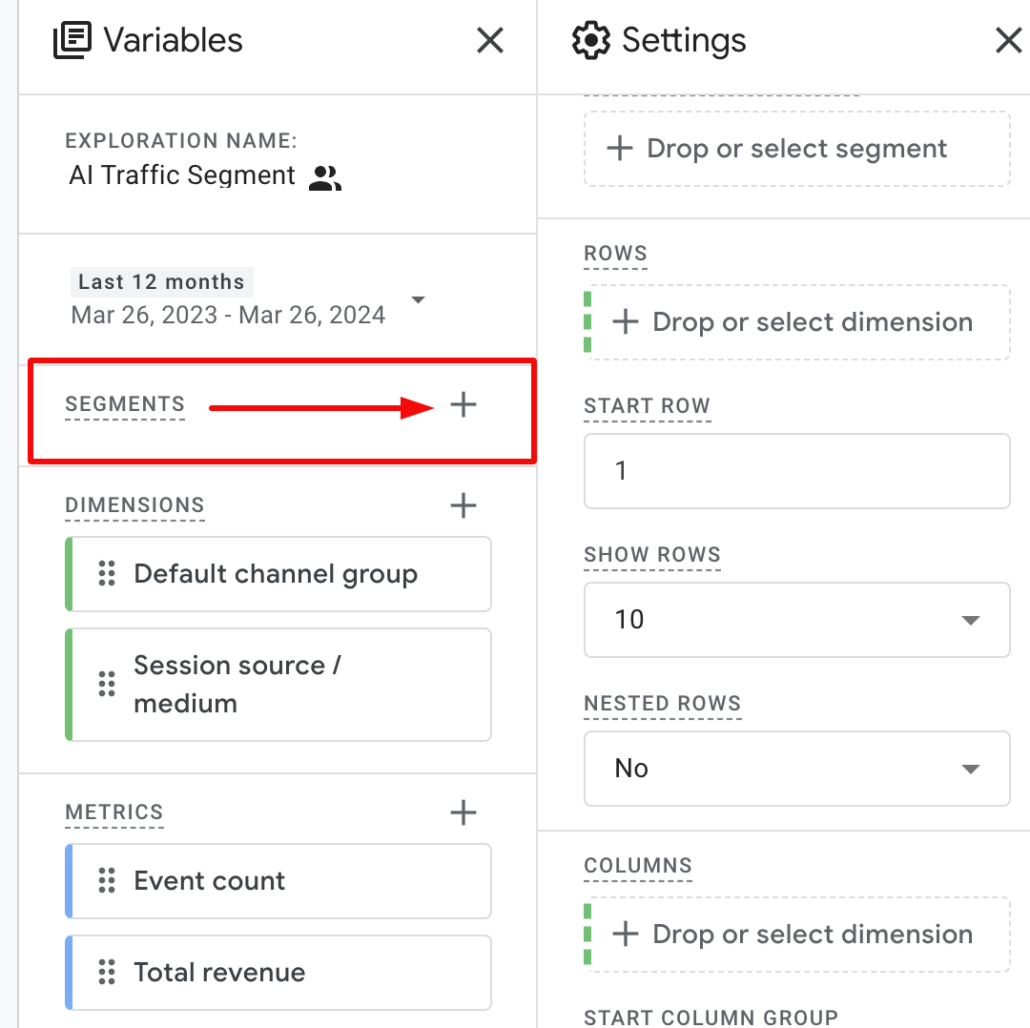
The second method for tracking traffic coming from AI chatbots is to create a segment in an Exploration report.
Start by creating a new Exploration report. Let’s call it the ‘AI Traffic Segment’.
Build a new segment by clicking on the plus sign next to SEGMENTS.
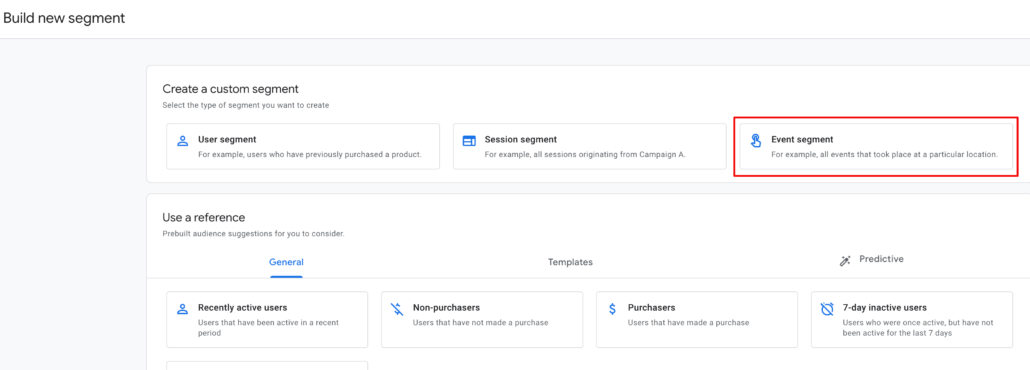
In the ‘Build new segment’ section click on the create ‘Event segment’ button.
Under ‘Add a new condition’, find ‘Page referrer’ and then apply the following filter: Page referrer matches regex .gpt.|.chatgpt.|.openai.|.neeva.|.writesonic.|.nimble.|.outrider.|.perplexity.|.*google.bard.|.*bard.google.|.bard.|.edgeservices.
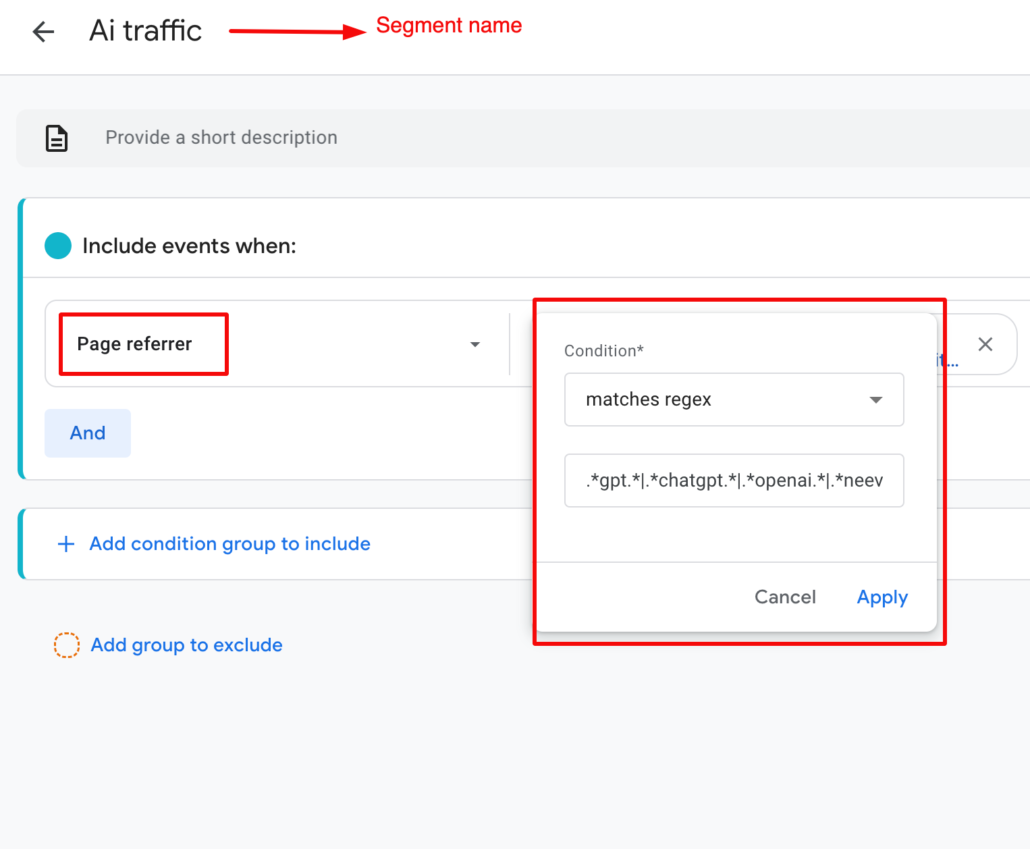
Name your new segment (I called it AI Traffic) and then save and apply it to your report.
Use ‘Page referrer’ as a dimension in ROWS.
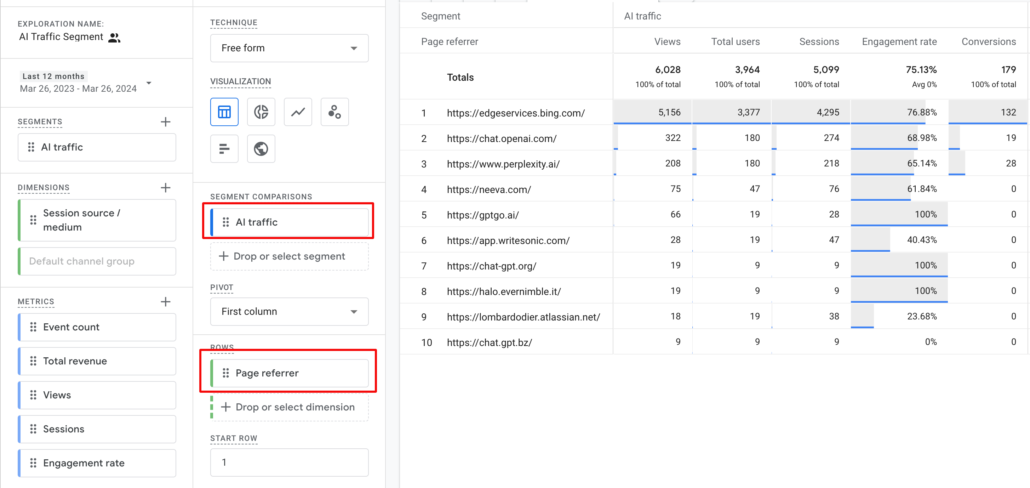
At this juncture, the AI referral traffic should appear on the chart.
I hope by now everything is clear, but as usual, if you have any questions, please comment down below, and I will try to get back to you as soon as possible.
FAQ
Referral traffic in GA4 refers to visits to your website that come from sources outside of search engines. When someone clicks on a link to your website on another website, it is considered a referral visit. Google Analytics 4 tracks referral traffic to help businesses understand which external sources are driving visitors to their site, enabling them to optimise their marketing efforts and partnerships effectively.
In GA4, session source refers to the origin from which a user arrives at your website or app during a specific session. This can include direct traffic (users who directly type in your website’s URL), organic search traffic (users who find your site through search engines), referral traffic (visitors who come from other websites, e.g. AI traffic), social media traffic, and more.
Understanding session sources allows businesses to analyse the effectiveness of various marketing channels and make informed decisions to improve their online presence.
In Google Analytics 4, ‘users’ and ‘traffic’ represent different metrics used to measure website or app engagement. ‘Users’ refer to the individuals who visit your website or app within a specified time frame, regardless of the number of sessions they initiate.
On the other hand, ‘traffic’ encompasses the overall volume of visits or sessions to your site, including both new and returning users. While users focus on the unique individuals interacting with your platform, traffic provides insights into the frequency and intensity of user engagement, helping online businesses measure the overall popularity and performance of their digital properties.



Leave a Reply